Security
- Security meant to be redundant (remember 2FA)
CS standards
- ISO/IEC 27001
- there is a whole family of these certificates
- Benefits
- secure all the information in all forms
- attack resilience
- protect what matters - and avoid what does not
- respond to evolving threats
- holistic approach
- links
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x792wXSeAhA
- ISO/IEC 27002
- Code of practice for ISC
- ISO/IEC 27701
- PIMS – Privacy information management system
- ISO 31000
- Risk management Practices
- PCI DSS
- Payment Card Industry Data Securit Standard
- for creditcards
- for whoever wants to process and store CC data
- PCI breach is alwas a GDPR breach
- 12requirements
- notorious
- NIS Regulations - Network Information Systems
- confidentiality - not available/disclosed to unauthorized ppl, entities or processes
- integrity - information is complete and acurate and protected from corruption
- availability - info is available and usable as and when authorized user needs it
- SSAE SOC 2 Type I / II
- Audit system
- Trust Services Criteria - security controls
- FW, intruson detection, MFA
- CSA - Cloud Security Alliance
- for non-profit org
- cloud specific security controls
- Controls are mapped to standards, best practices and regulations
- enterprise architecture
- build a roadmap
CSF – Framework
- Purpose
- Governance
- org context, mission, goal
- Risk appetite
- roles of people
- policies according to the mission, risks and roles
- Identif
- assets
- data
- hardware
- software
- people identities
- assets
- Governance
- CIS - Center for Internet Security
- CIS CSC - Critical Security Controls
- categorized per company size
- for it pros
- got actionable items
- NIST RMF
- National Institute of Standards and Technology Risk Management Framework
- 6 steps
- NIST CSF
- Cyber Security Framework
- Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover
- Framework implementation tiers
- ISMS - InternetSecurity Management System
- Processes
CS Certifications
- CompTIA
- Network+
- A+
- Security+ - gatekeeper for many jobs, A-tier
- Defensive OSCP - A-tier
- ISACA
- CISSP - A-tier - the best
- Cloud
- CCSK - top tier
- CCSP - pretty similar
- Azure Security Engineer - A-tier
- Google professional cloud security engineer
- CCSK - top tier
SSL/TSL certificates
These are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. When installed on a web server, it activates the padlock and the https protocol (over port 443) and allows secure connections from a web server to a browser.
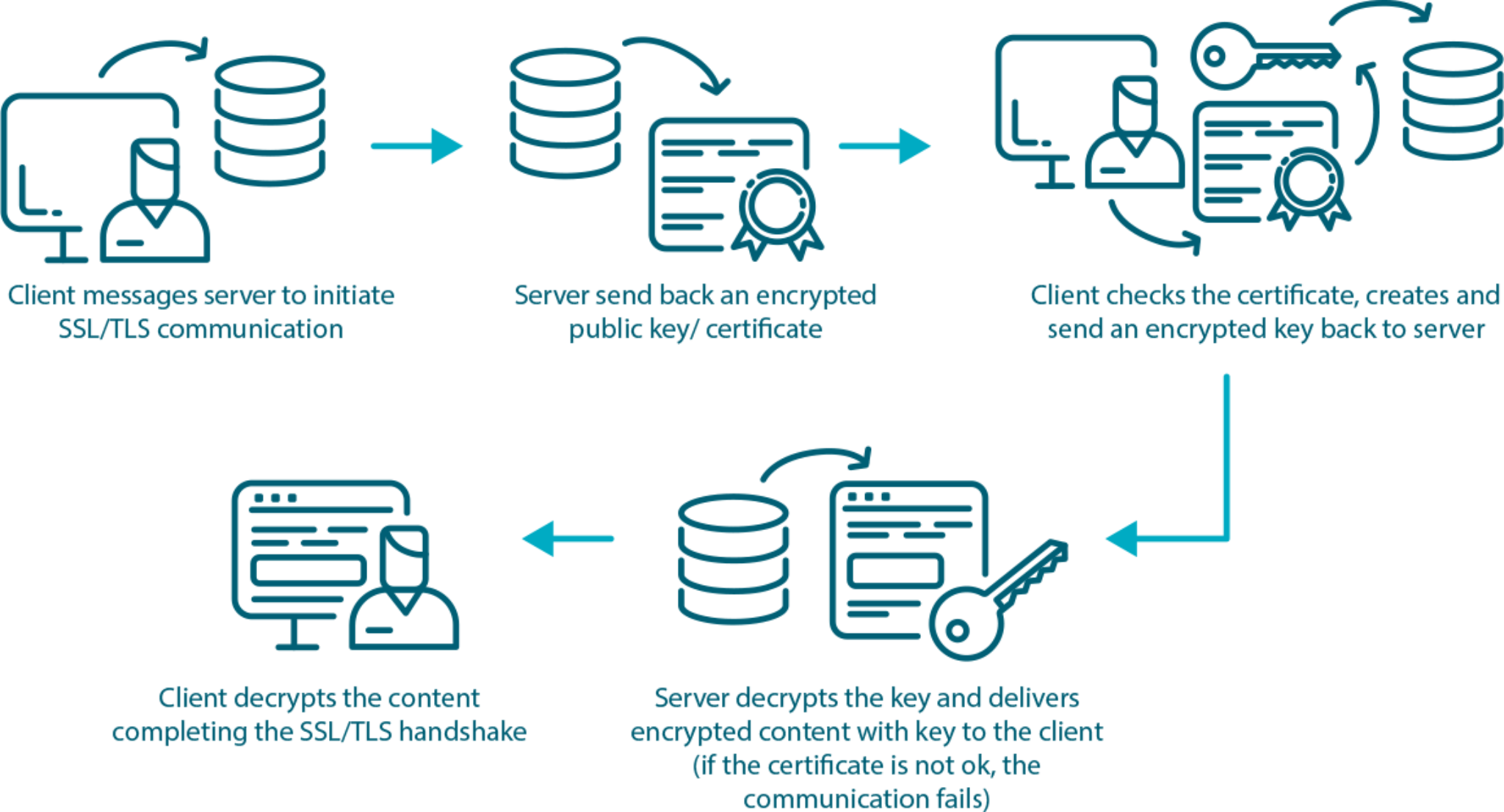
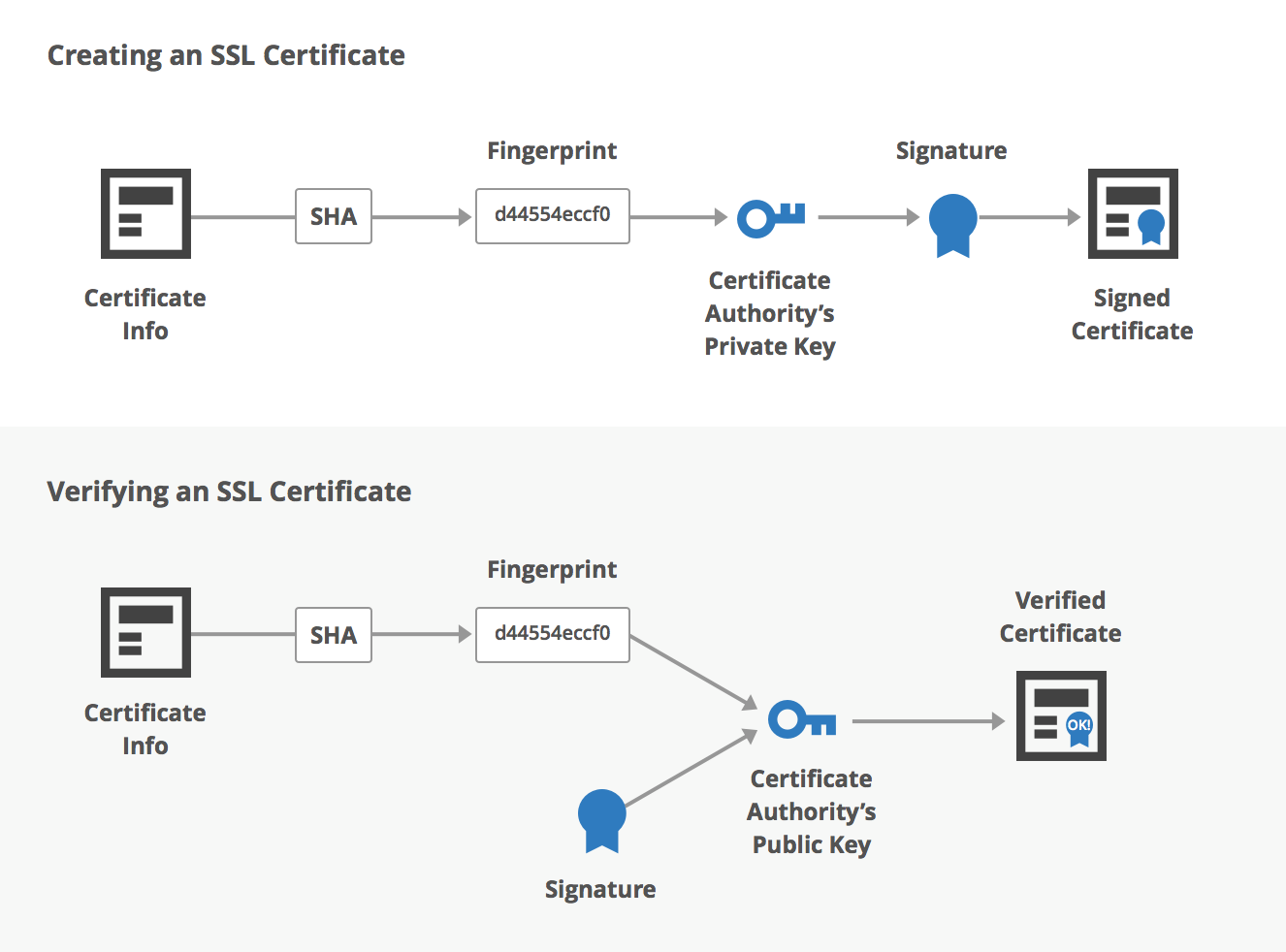
X.509
X.509 is a standard defining the format of public key certificates. These certificates are used in many Internet protocols, including TLS and SSL, which are the basis for HTTPS, the secure protocol for browsing the web.
In the context of X.509, an endpoint usually refers to a server or client that presents an X.509 certificate for authentication during a secure communication session. For example, when you connect to a secure website, the website’s server is an endpoint that presents an X.509 certificate to your browser to prove its identity.
In a broader context, an endpoint can also refer to a device or node that is an end point of a communication network, such as a computer, phone, or server. In the context of X.509, these devices might have their own certificates that they use to authenticate themselves to other devices or servers.
Zero trust security
Zero Trust Security is a model that assumes no trust for any entity—regardless of whether it’s inside or outside the network perimeter—trying to access network resources. Instead, every user, device, or system must be verified before access is granted.
Microsegmentation
This involves breaking up security perimeters into small zones to maintain separate access for separate parts of the network. For example, in a Kubernetes environment, network policies can be used to control traffic between pods.
Encryption
In a Zero Trust model, data should be encrypted at all times, both at rest and in transit. For example, in Google Cloud, customer data stored at rest is automatically encrypted without any action from the user.
Kubernetes
Apply all the security measures, just like onPrem
Image level
- scan images for vulnerabilities (by default done by DockerHub)
- use minimal images, like
alpine - use blank system, without building tools
- use a separate user for running the app
RUN adduser -D applicationuser RUN chown applicationuser:applicationuser ./executable RUN chmod +x ./executable USER applicationuser - disable privilege escalation on the pod level
kind: Pod spec: securityContext: allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
Authentication and Authorization
- RBAC
Role— what can you do with which resources in which namespaceClusterRole— same as role, but cluster wide, for admins.- Users
- there is no direct user object, instead there is:
- static tocken file
- certificates
- 3rd aprty ID services
- Binding — binds a role to a user
ServiceAccounts— for machines interaction. Ex: CI agent
- keep it as restricted as possible
Network
- by default each pod can talk to others
NetworkPolicyare there to limit it. On a network level 4. Not on App level 7- implemented by kubernetes nework plugin
ServiceMesh(Istio) allows us to go it on level 7, which is more convenient
In Transit
- The traffic in unencrypted by default
- Istio enables mutual TLS, so all the traffic is encrypted
At Rest
EncryptionConfigurationto solve the problem that Credentials, tokens, Private Keys are stored unencrypted by default- you still have to manage the encryption key and store it somewhere securely
- AWS KMS
- Hashi Corp Vault
- you still have to manage the encryption key and store it somewhere securely
etcd— unencrypted by default.- run it outside
- put it behind the firewall
- allow only access from API Server
- encrypt it
CI/CD
SecurityPolicies— to make developers follow security guidelines. Implemented by 3rd parties- hook into k8s
AdmissionControllerwhich is to decide if deployment can go through
- hook into k8s
Databases
Potential threats
- stealing data
- deleting
- corrupting/mocking
- encrypting and asking for ransome
- corrupting backups
Mitigations
- backup and restore
- immutable backups
Cloud
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jI8IKpjiCSM
SaaS PaaS
- Networks
- Containers
- Runtime
- Isolation IaaS
- Hypervisor and everything below it
Identity
Who?
- Identity
- Princiipal
- Role - role of somebody, an abstract Identity
What?
- Action
- with condition
When?
- Until when allowed?
Where?
- from specific CIDR
Auuthentication
- who?
Auuthorization
- what actions or resouurces
- permissions and privileges
- foor all the systems and adjecant systems
Auditing
- who did what in which system
PRO TIP: define your own roles, instead of using existing, to respect the principle oof least privelege
To learn
https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/cloudgoat https://learntocloud.guide/#/ https://cloudbreach.io/labs/ https://cyberwoxacademy.com/azure-cloud-detection-lab-project/ http://flaws2.cloud https://learntocloud.guide/#/
https://www.nojones.net/posts/breaking-into-cloudsec
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLDqMNdDvMsRn_ocTwQJR_eXMnv6K2I8eV
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RoZeVbbZ0o0&t=0s
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLDqMNdDvMsRndwjXFmus-p7p7Erd57Dvx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZzeMNGFv12A&t=0s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=op4mShTfNwk&t=0s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nz0CrOzeVl0&t=3893s
Links
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBf5lrmquYI
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jI8IKpjiCSM
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7ZqVRYVmRjM